Startups, Major Corporations Announce New Houston Energy 2.0 Projects in First Half of '21
Published Jun 11, 2021 by A.J. Mistretta
The pandemic, social influence and other factors appear to be accelerating the energy transition to a low-carbon future. Companies large and small, as well as governments around the world, are preparing for the change, and Houston is no exception. The acknowledged energy capital of the world is now working to position itself as the energy transition capital of the world.
Later this month, the Partnership will co-host The Future of Global Energy, presented by Chevron, a three-day conference in collaboration with the Center for Houston’s Future. On day one, the Partnership will reveal a blueprint for how Houston can guide the global energy transition—leveraging its knowledge and infrastructure. Other sessions will feature discussions on how to bolster carbon capture use and storage (CCUS) and hydrogen technologies in the region.
The Houston region is already attracting significant activity in the energy transition and energy 2.0 spaces. Following announcements from Greentown Labs and other players last year, momentum is ramping up in 2021. Here are a few projects we’re watching.
In February, Halliburton Labs announced the inaugural cohort of companies for its program that makes the oil field services giant’s labs, technical expertise and business network available to early-stage energy 2.0 companies. The goal is to help the companies prepare to commercialize and scale their technology. The initial cohort includes Nanotech Inc., Enexor BioEnergy, Momentum Technologies and OCO Inc.
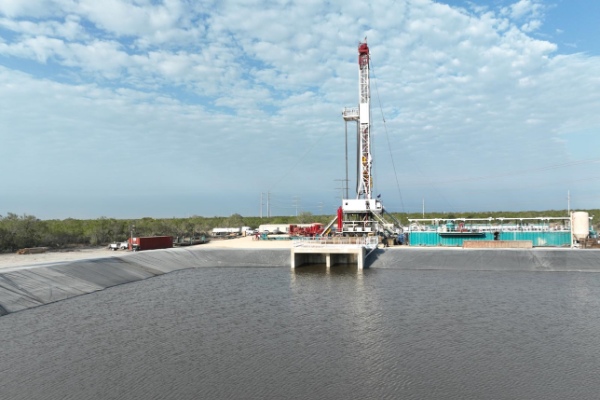
Media reports in March described a new 100-megawatt energy storage project being built in Angleton, about 40 miles south of downtown Houston. The project is registered to Gambit Energy Storage LLC, which is reportedly a subsidiary of Tesla. Battery storage initiatives are picking up across Texas and elsewhere around the country as companies work to increase the efficiency and capacity of large-scale power storage. The Angleton project could be enough to power 20,000 homes during the peak of summer.
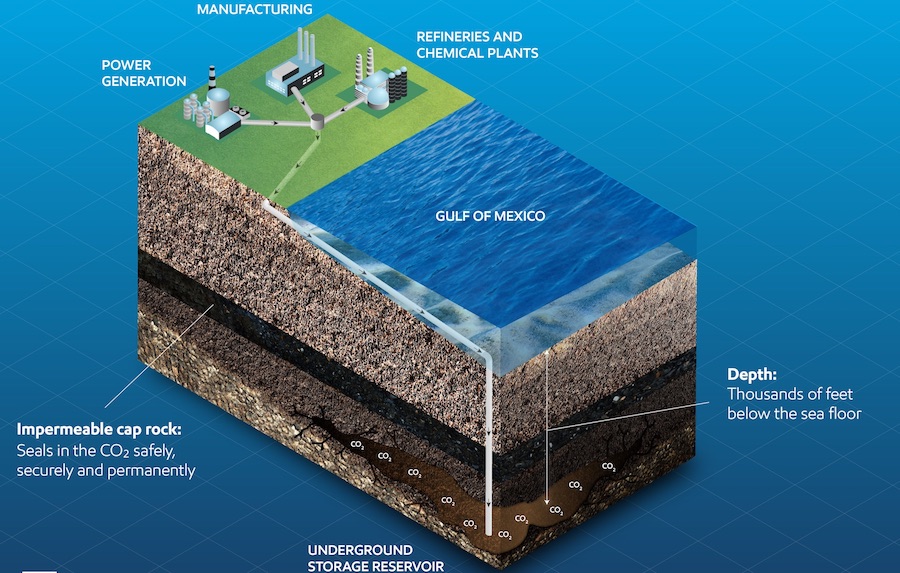
In April, ExxonMobil revealed a $100 billion proposal to create an innovation zone along the Houston Ship Channel that would capture carbon emissions from petrochemical, manufacturing and other plants. Those emissions would then be transported and stored in natural geologic formations on the sea floor of the Gulf of Mexico. Initial projections from the company estimate the project could capture and store about 50 million metric tons of CO2 a year by 2030. The project would require funding from both industry and government and is still in the feasibility stage.
Danish power company Ørsted is building Old 300, a 1.1-gigawatt solar PV, in Fort Bend County. The Old 300 Solar Center will cover an area of 2,800 acres and use approximately 1 million bifacial modules. The company said Old 300 will create a dependable source of income for the ranches that lease their land for the project. "With its location close to Houston, Old 300 will further diversify our onshore footprint into a premium market with strong long-term fundamentals." said Vishal Kapadia, chief commercial officer for onshore with Ørsted. "We're excited to add another large-scale, attractively contracted solar project to our portfolio. Solar is the fastest-growing power generation technology in the world and will continue to play a key role in our growth going forward."
Houston bio-manufacturing company Solugen is working on a project to create a new bio-based manufacturing process for a specialty chemical. The zero-carbon process for creating glucaric acid, which is a useful anti-corrosive agent, could represent a lucrative new product line for Solugen and set a roadmap for other low-carbon or no-carbon chemical manufacturing.
Cemvita Factory, a Houston-based startup that uses biotech to convert carbon dioxide emissions into a variety of useful chemicals, is plotting an expansion. The company said in May that it would more than triple its current headcount of 30 as it scales up to meet growing demand for services. Cemvita Factory uses synthetic biological processes to genetically alter microorganisms to absorb carbon dioxide and other molecules as feedstock. The altered microbes can then be turned into a variety of chemicals for industrial use, such as ethylene, which can be used to make plastics.
These are just a handful of the energy 2.0 projects happening across the Houston region. To learn more about the role such companies will play in the energy transition and how Houston is positioned to lead the effort, register today for The Future of Global Energy, presented by Chevron.
 The Houston Report
The Houston Report