Houston in 1969: A Look at the City Then and Now
Published Jul 01, 2019 by A.J. Mistretta
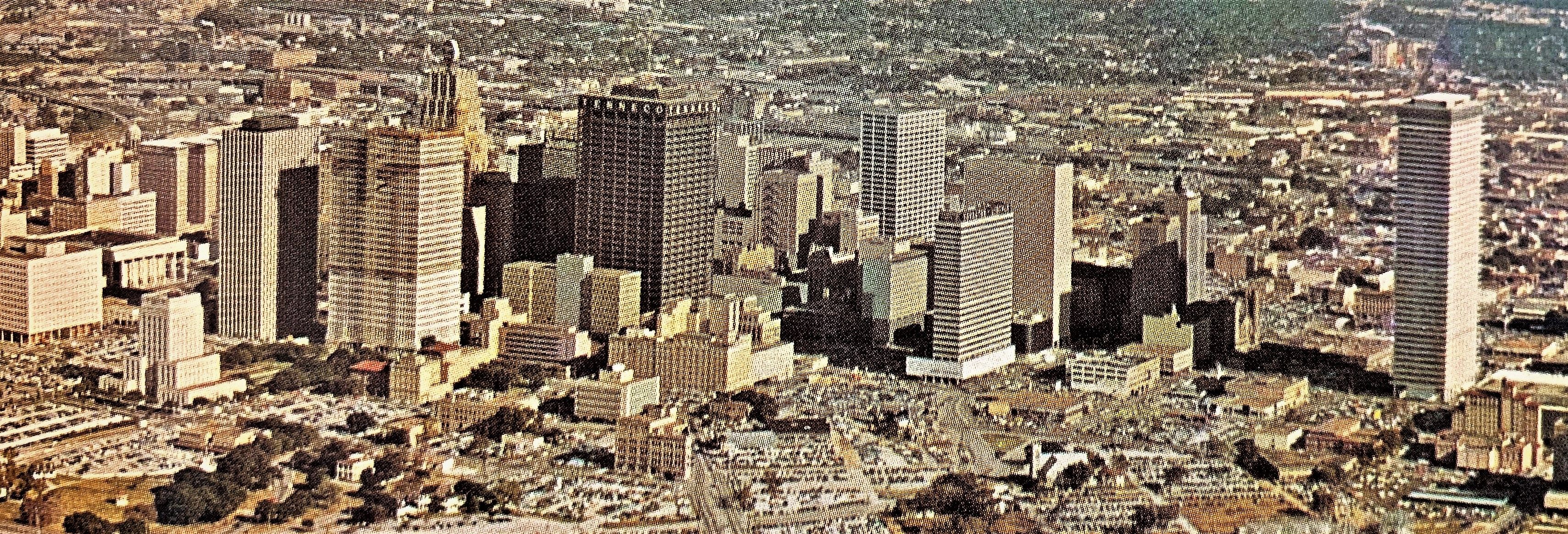
Fifty years ago, Houston was the sixth largest city in the U.S., home to the nation’s newest international airport and NASA’s Manned Spacecraft Center (later Johnson Space Center). The year 1969 brought the historic Apollo 11 mission that carried the first humans to the moon—a monumental achievement led in part by scientists based in Houston.
As the city celebrates that golden anniversary this summer, the Partnership decided to look at Houston, then and now.
Population and Land Area
The size of the city has expanded significantly in the last 50 years—both by land area and population. Houston proper encompassed 453 square miles in 1969. Today, at 665 square miles, the city of Houston could contain the cities of New York, Boston, San Francisco, Washington D.C. Seattle and Minneapolis—with a bit more room to spare.
The population within the city itself was 1.3 million people in 1969. That’s jumped to 2.31 million today as Houston surpassed other major cities to become the 4th most populous in the country. Even more impressive is the population growth of the metropolitan area, which has increased from 1.94 million in 1969 to 7.0 million today.
Economy
That tremendous population growth has spurred the economy of our region. Total employment in the Houston metro area was 853,900 in 1969. Today, that has more than tripled to 3.1 million jobs. And while inflation obviously plays a large role in salaries, it’s worth noting that total wages in the region have grown from $6.4 billion in 1969 to more than $195 billion today.
Certainly, some industries in Houston have grown faster than others, while a few such as digital technology barely existed at all back in 1969. One sector that’s seen a near tripling in the number of active companies is manufacturing, which has expanded from 2,608 firms across the region in 1969 to 6,388 such companies, according to the latest figures. However, the number of workers in the sector has increased by just 53% to 224,708 during that period—indicative of an industry where automation has aided production increases without a corresponding need for personnel.
Transportation, Trade and Logistics
The Port of Houston and other ports in Southeast Texas have long been significant economic forces for the region. Trade once dominated by agricultural products now includes fuel, petrochemical products and plastics. In 1969, the Port of Houston was the third largest in the U.S. by total tonnage moved, with total imports valued at $741 million and exports valued at $1.5 billion. In 2018, the port was No. 1 by tonnage with imports valued at $69 billion and exports valued at $90.2 billion.
Air travel has come a long way in the last 50 years as well. The Houston Intercontinental Airport (later George Bush Intercontinental Airport) opened in June 1969, joining the existing Houston International Airport (later William P. Hobby Airport). Passenger air travel was still in its early stages, but that year the two airports logged a combined 4.5 million passengers. Last year, a record 58.3 million passengers moved through the two airports.
Houston highways have dramatically expanded to keep up with the region’s growing population. In 1969 there were roughly 390 miles of state-managed highways across Harris County. Today, there are nearly 1,300 miles of such highways and interstates in the county and many of those that existed 50 years ago have been widened to accommodate more vehicles.
TMC and Hospitality
Through the decades, the Texas Medical Center has become a major economic engine for Houston—it’s now the eighth largest business district in the nation with an estimated GDP of $25 billion. TMC was already an emerging force in 1969 with 23 different institutions and nearly 14,000 employees. Today the 1,300-acre campus is home to 61 institutions and 106,000 employees.
Nearly two decades before the George R. Brown Convention Center would be completed, Houston wasn’t the convention or tourism destination it is today. In 1969 the area had just 18,000 hotel rooms. By the time the city hosted its second Super Bowl in 2004, that number had grown to 44,000 hotel rooms. Today, Houston is home to more than 91,000 hotel rooms with hundreds more across the region currently under construction.
Education
Ensuring Houston has a strong next generation workforce has always been critical to the success of the region. Over the years, the number of institutions and the types of degrees and certifications available to students seeking a post-secondary education have increased. In 1969, just under 53,000 students were enrolled in 22 colleges and universities in and around Houston. Last year, roughly 430,000 students were enrolled in more than 40 two-year community colleges and four-year and above universities across the region.
Get more facts about Houston and its economy by visiting the Data section of this website.
 The Houston Report
The Houston Report