Axiom Space Completes First Mission to ISS; More Missions Ahead for Houston Aerospace Co.
Published Apr 27, 2022 by A.J. Mistretta
A Houston company is charting new territory in the rapidly evolving commercial aerospace sector after completing a historic mission.
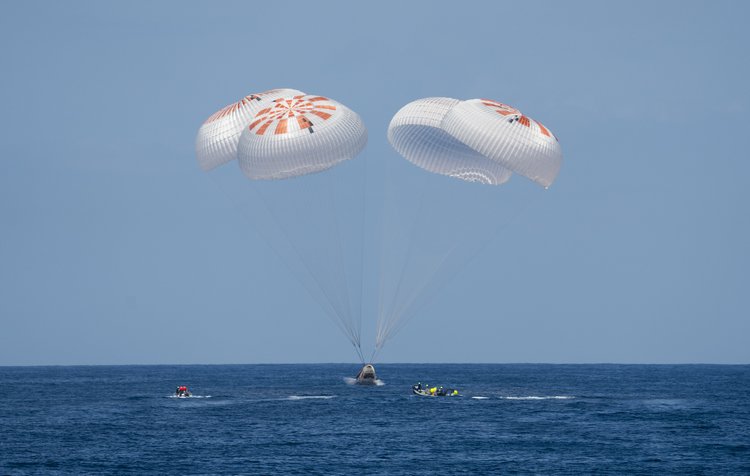
The crew of Axiom Mission 1 splashed down off the coast of Florida on April 25 inside a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft. The return of Axiom Space's crew to Earth concluded the first all-private astronaut mission to the International Space Station (ISS), paving the way for a new era in commercial spaceflight and research.
The 17-day mission 6.3 million-mile mission included 15 days aboard the ISS. A few highlights from the mission according to Axiom include:
- Ax-1 supported 26 science payloads and technology demonstrations that had been curated with leading academic and research partners around the globe, including the Mayo Clinic, Montreal Children’s Hospital, Cleveland Clinic, and the Ramon Foundation.
- Research investigations were conducted in collaboration with Axiom’s partners such as studying self-assembling technology for future space habitats, devices to purify air on space stations, and more.
- The Axiom astronauts served as research subjects to better understand the impacts of microgravity on the human body, as well as methods for maintaining connectedness to loved ones on Earth during space travel.
- The Ax-1 crew shared the excitement of expanded access to space with a new generation of space explorers, participating in over 30 STEAM (science, technology, engineering, art and math) engagements. Outreach efforts were conducted in English, Hebrew, Spanish, French, and Arabic
“Axiom Space is incredibly proud of this mission and these astronauts, whose training rigor and commitment to a robust research portfolio set the standard for future private spaceflight,” said Michael Suffredini, President and CEO of Axiom Space, which is building its new headquarters at the Houston Spaceport. “The Ax-1 mission is a pathfinder, showing the value of this new method of access to orbit and progress toward Axiom Station, a next generation platform in which the benefits and products of life, work and research in space will be available to a greater number of people.”
Ax-1 is the first of several planned Axiom missions to the ISS and is an important step for Axiom Station, the first commercial space station that will serve as a global academic and commercial hub. The station will be constructed in Houston.
Axiom is a major player in Houston’s bid to regain prominence in the aerospace sector. The creation of the Houston Spaceport at Ellington Airport is galvanizing activity and creating synergies between private companies, NASA and researchers.
Learn more about efforts underway to leverage Houston's rich aerospace history to grow the emerging commercial sector.
 The Houston Report
The Houston Report